Key points:
- Credit Suisse opened two accounts for Billy Rautenbach, a notorious mining magnate who was later sanctioned for his role in Zimbabwe’s 2008 election.
- The accounts were opened weeks before a mining deal funneled $100 million to Robert Mugabe’s government, which reportedly funded violence that helped him win the election.
- The sanctioned Rautenbach was able to sell his shares from the deal for a huge profit, but the mine was left undeveloped for over a decade.
In 2008, Zimbabwe was at a turning point. President Robert Mugabe faced electoral defeat by pro-democracy challengers for the first time in two decades. Suddenly, his cash-starved regime received a surprise $100 million, which it allegedly funneled into a violent campaign that enforced the status quo, and kept Zimbabwe on the road to an economic disaster from which it is yet to recover.
Now, leaked data from Swiss banking giant Credit Suisse has shed new light on the role the bank played in the deal that saved Mugabe from potential defeat, and blocked an opportunity for political and economic reform.
The $100 million came from the sale of platinum mining rights that Mugabe’s government had quickly appropriated, then given to a company owned by Muller Conrad “Billy” Rautenbach, a longtime friend of the regime. Mugabe’s regime used the proceeds of the deal to pay for the president’s campaign of violence, according to multiple reports.
Rautenbach and Credit Suisse knew each other well. They both owned a large share of the same company: Central African Mining and Exploration Company (CAMEC). By mid-2007 the bank owned six percent of CAMEC through its London-based investment subsidiary, Credit Suisse Securities Ltd.
Credit Suisse touted Rautenbach as a key asset in the region. Its mining analysts promoted CAMEC in the press and in briefing notes, telling investors the company was a “new major in the making,” and a possible rival to mining behemoth Xstrata.
Credit Suisse also gave CAMEC, which was listed on London’s Alternative Investment Market index, a $60 million line of credit, which the company fully used.
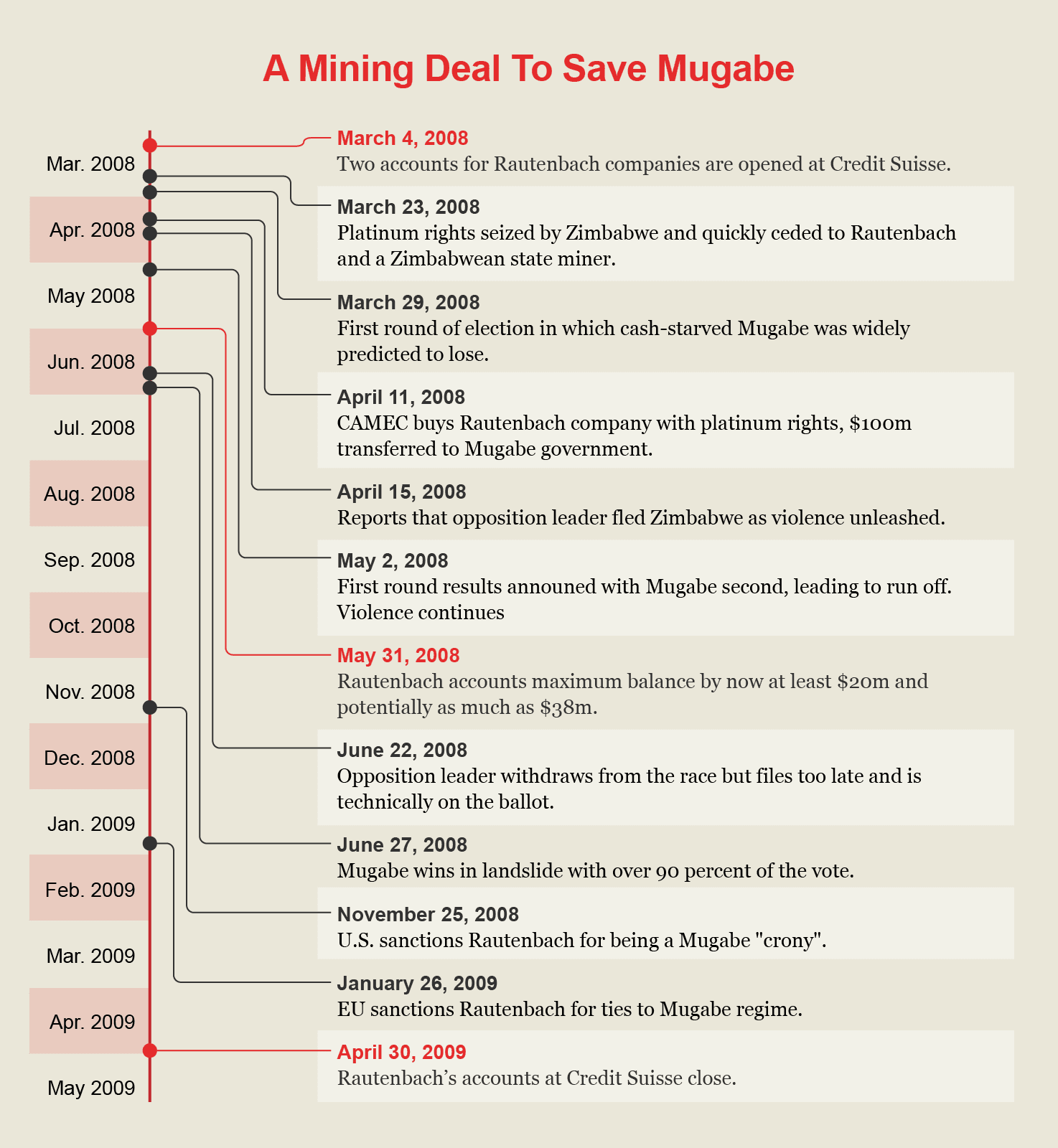
On March 4, 2008, a chain of events began that would quickly get the Mugabe administration the money it needed for its re-election campaign while also earning Rautenbach a sizable profit. It started when Rautenbach opened two accounts with Credit Suisse, according to leaked bank records that are part of the Suisse Secrets investigation, coordinated by OCCRP and based on a huge trove of banking data leaked to Süddeutsche Zeitung.
The Suisse Secrets Investigation
Suisse Secrets is a collaborative journalism project based on leaked bank account data from Swiss banking giant Credit Suisse.
The data was provided by an anonymous source to the German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung, which shared it with OCCRP and 46 other media partners around the world. Reporters on five continents combed through thousands of bank records, interviewed insiders, regulators, and criminal prosecutors, and dug into court records and financial disclosures to corroborate their findings. The data covers over 18,000 accounts that were open from the 1940s until well into the last decade. Together, they held funds worth more than $100 billion.
“I believe that Swiss banking secrecy laws are immoral,” the source of the data said in a statement. “The pretext of protecting financial privacy is merely a fig leaf covering the shameful role of Swiss banks as collaborators of tax evaders. This situation enables corruption and starves developing countries of much-needed tax revenue.”
Because the Credit Suisse data obtained by journalists is incomplete, there are a number of important caveats to be kept in mind when interpreting it. Read more about the project, where the data came from, and what it means.
Then, two weeks later, the Zimbabwean government strong armed mining company Anglo American into handing over a tranche of land that included the rights for mining platinum there. The government immediately transferred those rights to Rautenbach’s offshore company and a state mining company.
CAMEC announced a few days later, on March 28, that it would issue 200 million shares of its stock worth about 100 million British pounds ($1.99 million). One of the buyers that helped finance the controversial deal was reportedly Credit Suisse, which bought an unknown number of shares. The majority of shares was bought by Och-Ziff Capital Management Group, a U.S.-based hedge fund (now called Sculptor Capital Management).
Two weeks later, on April 11, 2008, CAMEC bought out Rautenbach’s company for $5 million and 215 million CAMEC shares. CAMEC provided its new company with $100 million to enable it “to comply with its contractual obligations” to Mugabe’s government, according to CAMEC’s stock market filings. But the money does not appear to have been used for meeting any obligation, or doing any mining. Instead, the company was widely reported to have transferred the funds to Mugabe’s ZANU-PF political party.
With a flurry of activity, the entire process was completed in less than three weeks. CAMEC had its mining rights, the Mugabe regime had $100 million, and Rautenbach had pocketed a substantial sum.
A former executive at the mining company that had to give up the platinum rights, speaking anonymously due to the risks posed by commenting, said it was obvious they had to comply.
“There was no doubt our presence [in Zimbabwe] was under threat had we not agreed to the surrender of land,” he said, adding that Rautenbach and CAMEC “relied solely on…political connections.”
Documents from a U.K. government corruption investigation looking at mining deals in central Africa, obtained by OCCRP, showed CAMEC may have acquired “tainted assets from those who engage in corruption.”
The $100 million arrived within weeks of Mugabe losing the first round of elections to opposition leader Morgan Tsvangirai. With a run-off vote looming, and money in the bank to pay thugs and supporters, the ZANU-PF set to work delivering on a threat to punish anyone who betrayed them at the ballot box.
Within days of the money arriving, a three-month campaign of terror had started.
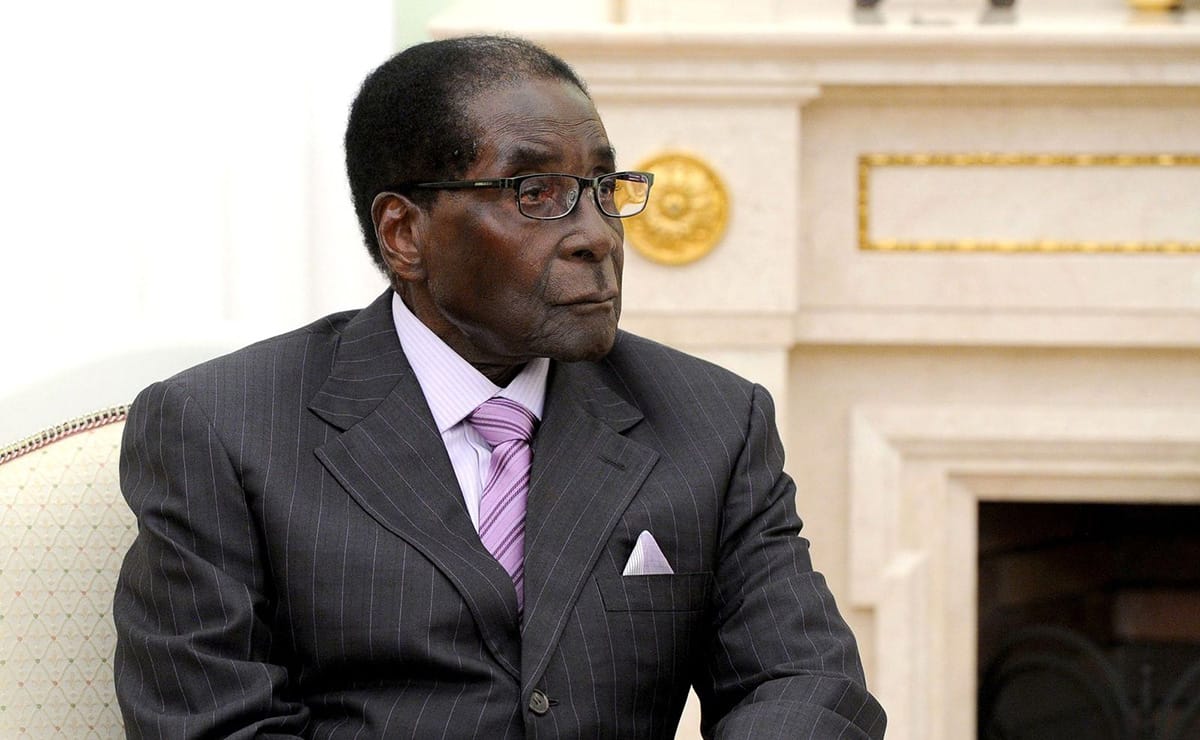

Soldiers and armed gangs unleashed Operation Makavhoterapapi? (‘Where did you put your vote?’), in which more than 100 people were killed and over 1,000 attacked. Opposition leader Tsvangirai was forced to flee the country only four days after the $100 million arrived with the regime. With the opposition decimated by violence, Mugabe went uncontested into the next round.
“That money totally brought about all the heartache, pain, gerrymandering, violence, intimidation, repression that took place at the 2008 election,” said Roy Bennett, a former anti-Mugabe politician, on a Zimbabwean radio show in 2012. “[The election violence] is directly linked to that $100 million.”
Three days after the platinum deal closed, and as Zimbabwe descended into violence, a Credit Suisse research paper lauded CAMEC as one of its “African 20” stock picks.
There is no evidence that Credit Suisse knew about the planned corruption but it should have seen that the deal was suspicious. A classified U.S. State Department cable, sent May 23, 2008, and later released by Wikileaks, described the sale as a “swiftly concluded and murky deal.”
Mining Controversy
Rautenbach was already a controversial figure when Credit Suisse opened his accounts in early March 2008, having fled fraud charges in South Africa and been deported from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) for mining-related corruption. A 2006 U.N. report questioned Rautenbach’s integrity and criticized inadequate due diligence on his DRC mining deals.
Rautenbach’s accounts at Credit Suisse were open for several months after both the U.S. and EU sanctioned him for his role in subverting Zimbabwe’s democracy. It’s not clear if Rautenbach closed them or if the bank acted.
“It beggars belief that Credit Suisse continued to provide Rautenbach with banking facilities given the furor created by CAMEC gifting $100 million to Mugabe,” said Anneke Van Woudenberg, executive director of U.K.-based corporate watchdog RAID.
“Credit Suisse’s process to verify its clients was either woefully inadequate or completely ignored,” she said.
By the end of May 2008, the two Rautenbach accounts were worth more than $20 million, and potentially as much as $38 million, though OCCRP cannot assess whether these funds were tied directly to the platinum deal. The accounts were finally closed in April 2009, after U.K. authorities froze Rautenbach’s holdings in CAMEC.
By then, Mugabe was well into his fifth term, and Rautenbach had already profited from the platinum sale.
Backing CAMEC and Rautenbach
Even before CAMEC took control of the Zimbabwe platinum mine, the company was growing rapidly during the height of the early 2000s commodity boom. The company’s share price soared and by 2007 it had attracted a range of large institutional investors eager to capitalize on rising metals prices.
A business intelligence consultant with knowledge of Rautenbach’s dealings, who requested anonymity for professional reasons, said companies like CAMEC relied on backing from institutional banks and investors to secure mining deals.
“[The banks and companies] bring not only capital, but high level connections and influence. Investors in CAMEC were desperate to defend CAMEC and Rautenbach.”
By late 2008, one of Credit Suisse’s leading Africa mining analysts had even joined CAMEC as its head of investor relations.
Rautenbach also held a major stake in CAMEC and was responsible for most of its day-to-day operations in DRC, where he had long been a key player in the troubled mining sector –– often acting on behalf of Mugabe’s regime.
“[Banks and companies] liked that Rautenbach got things done – he was the hands-on organizer,” said the business intelligence consultant.
To finance the platinum rights acquisition, CAMEC had tapped both old and new investors. Credit Suisse bought in, but the main investor was a New York-based hedge fund then called Och-Ziff Capital Management Group, which would later become enmeshed in a lawsuit that shed light on the Zimbabwe deal.
In September 2016, Och-Ziff admitted to bribing officials in countries across Africa, from DRC to Libya, and agreed to pay a $412 million fine to the U.S. Department of Justice to settle pending criminal charges.
Documents from that case describe a March 2008 visit to DRC and Zimbabwe by an Och-Ziff executive. He met with Rautenbach, described in documents as a “Zimbabwe shareholder” of a “London stock exchange-listed mining company with operations in the DRC.” The documents corroborate Rautenbach’s role in the platinum rights deal and the $100 million that reportedly made its way to Mugabe.
According to media reports, the Och-Ziff executive’s trip to Zimbabwe and DRC was organized by Credit Suisse.
Credit Suisse did not respond to questions about specific accounts or customers. The bank said it “operates its business in compliance with all applicable global and local laws and regulations” and that it had strengthened its “risk management framework and control systems.”
Rautenbach did not respond to questions.
Sanctions Ignored
In November 2008, once the scale of Zimbabwe’s election violence had become clear, the U.S. Treasury Department sanctioned several Mugabe “cronies,” including Rautenbach and one of his companies, accusing him of supporting mining deals that benefitted corrupt officials.
The EU followed suit in January 2009, sanctioning Rautenbach and hundreds of Zimbabwean officials and enablers. The EU lifted its sanctions in 2012, while U.S. sanctions remained in place until 2014. Rautenbach had reportedly lobbied both the U.S. and EU to get off the blacklists.
In September 2009, Kazakh mining company Eurasian Natural Resources Corporation (ENRC) agreed to buy CAMEC for an estimated $955 million, delivering a huge payday to its shareholders, including Rautenbach and Credit Suisse.
Rautenbach never publicly revealed how much he profited from the sale to ENRC, but OCCRP analysis of the share price shows that he would have made at least $99 million, on top of the $5 million he earned when the platinum rights were sold.
CAMEC’s dealings in Zimbabwe were so dubious that ENRC was required to file a Suspicious Activity Report to U.K. authorities when it bought the company, according to court documents OCCRP obtained.
The report said CAMEC “might have been involved in breaches of Zimbabwe sanctions” and “might have made unlawful payments in order to secure or retain its mining licenses.”
Because Rautenbach was under EU sanctions at the time, ENRC had to get special permission from U.K. authorities to buy out his CAMEC shares. Though the U.K. Treasury did not confirm the waiver was granted, ENRC acquired 100 percent of CAMEC.
By the end of 2013 ENRC had delisted and left London after the U.K.’s Serious Fraud Office opened an investigation into its business in Africa.
The platinum site in Zimbabwe was left undeveloped for over a decade, and no platinum appears to have ever been mined.
The OCCRP’s story READ HERE.

